
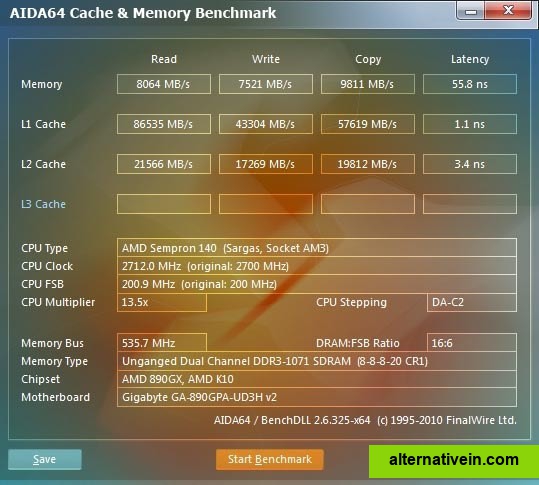

The Memory Latency benchmark measures the typical delay when the CPU reads data from system memory.
#Aida 64 code#
The code behind these benchmark methods are written in Assembly and they are extremely optimized for every popular AMD, Intel and VIA processor achieveablecore variants by utilizing the appropriate x86/圆4, x87, MMX, MMX+, 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2, SSE4.1, AVX, AVX2 and AVX-512 instruction set extension. Memory bandwidth benchmarks (Memory Read, Memory Write, Memory Copy) measure the maximum achievable memory data transfer bandwidth. Both FP32 and FP64 Ray-Trace test is HyperThreading, multi-processor (SMP) and multi-core (CMP) aware. The code behind this benchmark method is written in Assembly, and it is extremely optimized for every popular AMD, Intel and VIA processor core variants by utilizing the appropriate x87, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, AVX, AVX2, XOP, FMA, FMA4 and AVX-512 instruction set extension. These benchmarks measure the single and double precision (also known as 32-bit and 64-bit) floating-point performance through the computation of a scene with a SIMD-enhanced ray tracing engine. It also supports multi-processor, multi-core and HyperThreading enabled systems. These benchmarks are synthetic, so their results show only the theoretical (maximum) performance of the system.ĬPU and FPU benchmarks of AIDA64 Extreme are built on the multi-threaded AIDA64 Benchmark Engine that supports up to 1280 simultaneous processing threads. Benchmark pages of AIDA64 Extreme provide several methods to measure system performance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
